Jaimie Barnes
Physics 212x
| Home |
Parts |
How it Flies |
Steering |
Watch |
Bibliography |
HOW IT FLIES
The Envelope of the balloon is filled with the
heated air heated by the burner, that is a gas that is less
dense than the surrounding air. This lighter air gives the
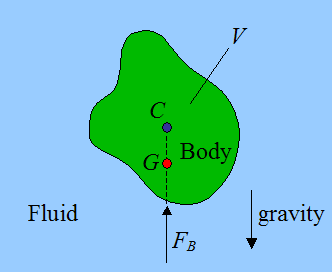
balloon buoyancy and causes it to rise. The principle behind
this is Archimedes' principle which describes how a body in a
fluid (which air is considered), is acted upon by a force equal
to the weight of the fluid displaced by the body.

Image From
Volume 'V' is the volume of the balloon, equal to the volume
displaced by the balloon.
Vair displaced=Vballoon
The force FB is the upward buoyant force equal to the
weight of the cooler air displaced by the balloon.
FB=Masscool air displaced
The cooler surrounding air has a greater mass than the heated
air, so FB is greater than the mass of the balloon.
When it exceeds the weight of the heated air, the envelope,
basket and everything inside it, then it will lift off of the
ground.
FB>Weight total balloon
Since all of this mass is near the base of the balloon it
remains stable throughout the flight.