a storm is coming
What is a geomagnetic storm and how does it effect earth?
According to the Space Weather Prediction Center, a geomagnetic storm is " a major disturbance of Earth's magnetosphere that occurs when there is a very efficient exchange of energy from the solar wind into the space environment surrounding Earth." This exchange is so powerful, it is able to break through parts of Earth's geomagnetic field that are impenetrable to the typical solar wind it encounters.
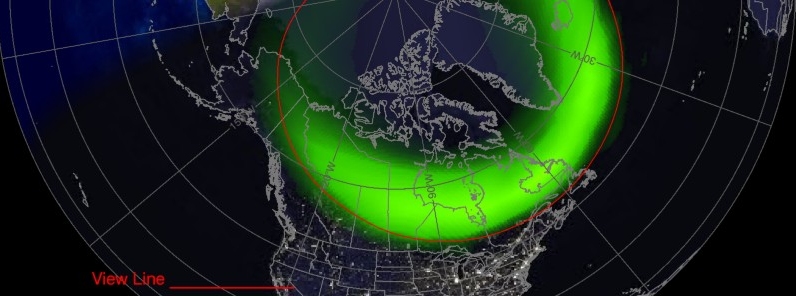
photo cred: https://watchers.news/data/thumbs/796_296/2017/02/geomagnetic-storm-february-24-2017.jpg
This storm creates beautiful Aurora, able to be seen even near to the equator in some cases. However, it does more than that. These storms can be dangerous as well as beautiful. Again quoting NWPC:
During storms, the currents in the ionosphere, as well as the energetic particles that precipitate into the ionosphere add energy in the form of heat that can increase the density and distribution of density in the upper atmosphere, causing extra drag on satellites in low-earth orbit. The local heating also creates strong horizontal variations in the in the ionospheric density that can modify the path of radio signals and create errors in the positioning information provided by GPS. While the storms create beautiful aurora, they also can disrupt navigation systems such as the Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) and create harmful geomagnetic induced currents (GICs) in the power grid and pipelines.Thus, these storms, although vicious, contribute to the sight of the Aurora... even if you don't live near the poles.