| Title Page |
| Page 1 |
| Page 3 |
| Page 4 |
| Bibliography |
Gravity

http://hashem.com/the-hidden-cosmic-code-of-gravity/
Gravity is the force that holds mass together. When an object has more mass it also possesses a larger force. We know this concept from Newton's 2nd Law, Force is equal to mass times acceleration. In regards to gravity, we tend to refer to acceleration as gravity which has a constant value of 9.81 m/s^2. When we walk on the Earth's surface, we are constantly both being pulled by Earth's gravity and are pushing back on it. This is according to Newton's 3rd Law which states that with every action force there is an equal and opposite reaction force.
Orbit
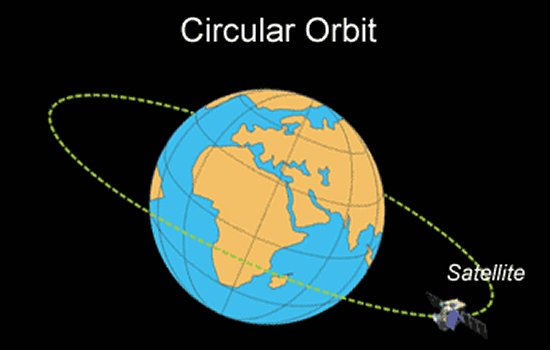
http://www.aerospaceweb.org/question/spacecraft/q0164.shtml
An orbit is the path that an object in space takes around another. Our planet orbits the sun and our satellites, natural or man made, orbit the Earth. This is what spacecrafts have to break free of in order to escape Earth's gravitational pull. Space is not a perfect vacuum; tiny particles do impact satellites and very slowly push them off course by creating a significant amount of drag. Anything that NASA or any other agency places in orbit will be affected by this and it's estimated that a space shuttle could theoretically stay in orbit for a month before the drag causes it to go off course.