Special
Relativity

According to
the National Center for Supercomputing Applications,
the Special Theory of Relativity postulates that
the speed of light is constant for all observers,
and all observers moving at constant speed
should observe the same physical laws (NCSA).
Through those ideas, Einstein found tha
t, "time intervals change according to the speed
of the system relative to the observer's frame
of reference" (NCSA).
This phenomenon is called time dilation, that
is, "a difference of elapsed time between two
events as measured by observers either moving
relative to each other or differently situated
from a gravitational mass or masses" (Wikipidia).
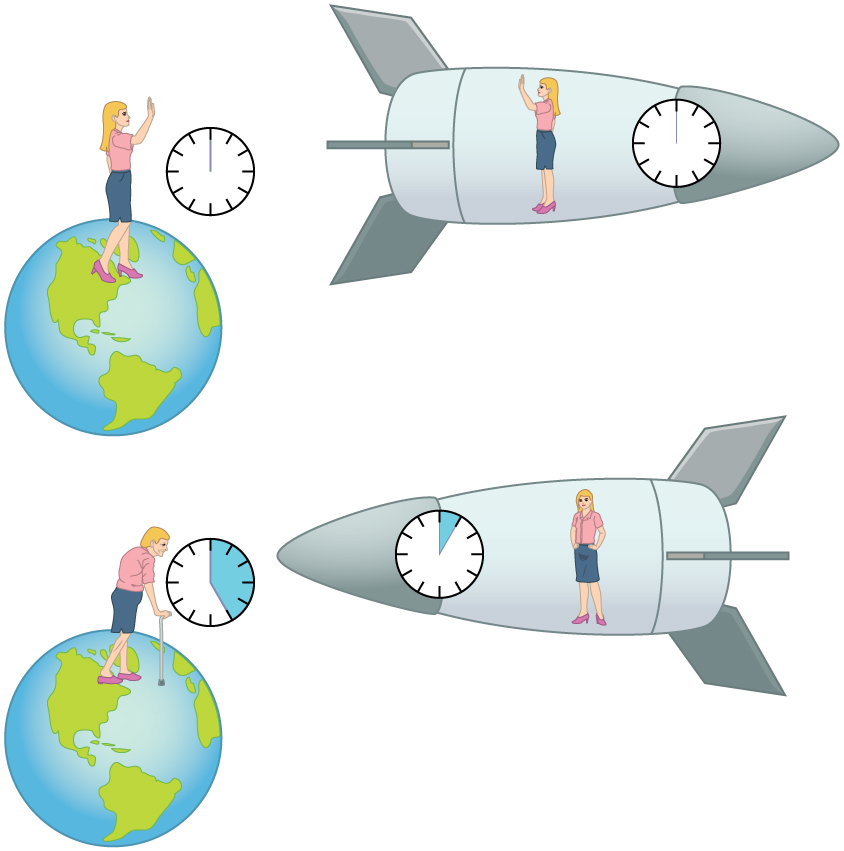
|
Here is a picture showing how
time dilation works:
- Both women start at the same time.
- The woman in the ship is moving much
faster relative to the woman on Earth.
- The elapsed time is different between
the two women.
- For every five hours that pass on
Earth, the woman on the spaceship
observes one hour passing.
|
http://philschatz.com/physics-book/contents/m42531.html
|
Through his discovery of the relativity of space
and time, Einstein also found that matter and
energy are equivalent. Thus his renowned
equation was formed:
The Special Theory of Relativity
was a tremendous breakthrough in physics, but
something was missing. It was, "limited to
bodies moving in the absence of a gravitational
field" (NCSA).
Ten studious years later, and finally
generalized his theory.
|