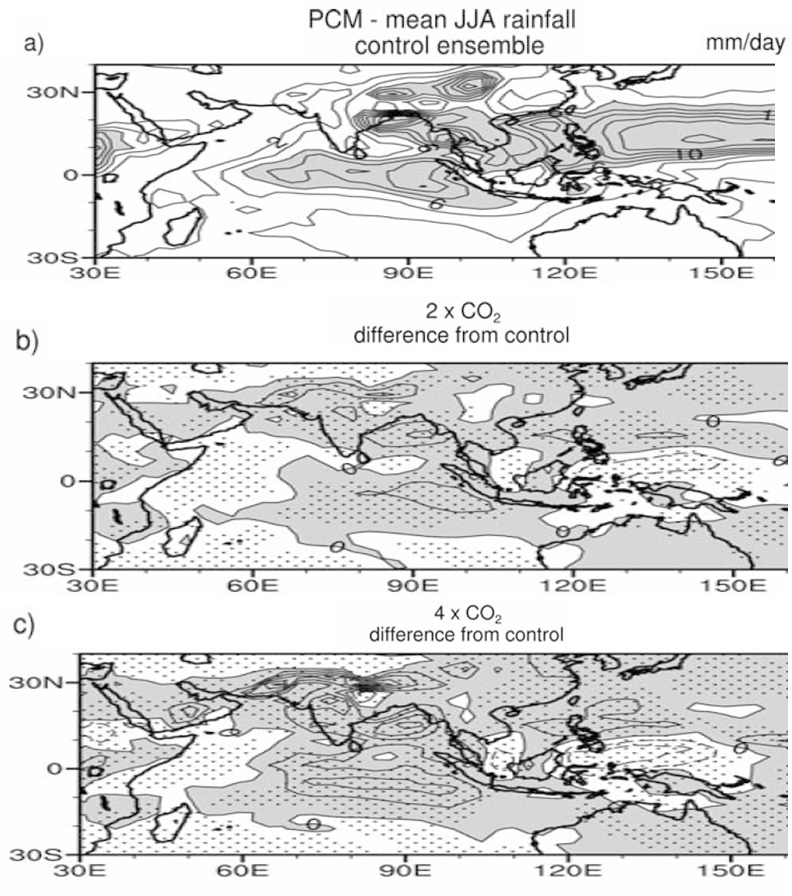
Meehl and Arblaster (2003) found out that summer monsoon precipitation and its interannual variability increase with increasing CO2 concentration by using the Parallel Climate Model (PCM)

(a) Summer mean rainfall averaged over a 300 year period in the control run of the PCM (coupled model) over south Asia, contour interval 2 mm/day, values greater than 6 mm/day shaded; (b) differences between 100 year stabilized 2XCO2 experiment and control precipitation, summer, contour interval 1 mm/day, positive areas shaded, stippling indicates areas exceeding 10% significance level from a student t test of the differences; (c) same as (b) except for 4 X CO2
Monsoon precipitation index increases about 9% in 2XCO2 simulation compared to control run whereas it increases about 19% and 10% in 4XCO2 compared to control run and 2XCO2 run