Process for Making Liquid Nitrogen

Liquid Nitrogen is created through a multistage processes which pulls the air around us, separates the different elements present in the air (largely nitrogen, oxygen, argon, water vapor, and carbon dioxide), and then converts nitrogen gas to its liquid form by cooling it below its boiling point. There are several methods in which to accomplish this but some are more affective then others due to the amount of demand for the product (liquid nitrogen) and also what the end product is going to be used for (how pure does the sample of nitrogen need to be).
The methods of creating liquid nitrogen only differ in the method by which the elements of air are separated. The process by which liquid nitrogen is formed from its gaseous state is more or less the same. The methods that are primarily used to separate the elements are: Cryogenic Air Separation, Absorption, and Membrane Diffusion.
Cryogenic Air Separation Steps (Practical for large scale industrial distribution of product)
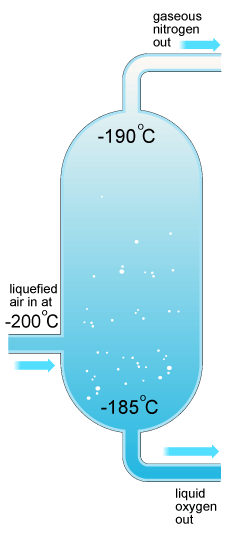
This method filters out impurities (elements other than Nitrogen) by using the elements’ boiling points.
· Dust is removed before entering by filters
· Water vapor is extracted from the air by using a multi-compression refrigeration cycle to cool and condense the water out of the air before moving on
· The air is sent to a container to extract the rest of the water vapor and CO2 , this is done by lowering the temperature in the container and freezing the CO2 and water vapor to the walls of the container, the left over elements (nitrogen, argon, and oxygen) are still in a gaseous state and are sent on to another process, the container is then warmed and the condensed CO2 and water are drained and vented from the container ( this is done with multiple containers so that while one is warming the other is going through the cooling process).
· At this point the temp of the remaining elements are brought to about -185oC which is below the boiling point of oxygen and near that of argon as well, this forces the two elements to the bottom of the container while nitrogen is left in a gaseous state leaving the top of the container (boiling points are in the table below).
Elements and Molecules Boiling Points ( oC ) % Contained in Air by Volume
Argon -185.8 0.93 Oxygen -183.0 20.95 Water Vapor 0 -------
Nitrogen -195.8 78.08 Carbon Dioxide -78.5 .038