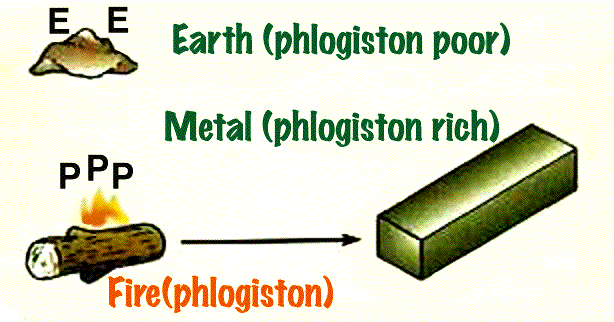
In early thermodynamics, the initial explanations of heat were confused with explanations about combustion. By the 17th century, phlogiston was considered to be substance of heat, like one of the classical four elements of the Greeks.
The caloric theory was produced by Lavoisier in the 1770's. In his papers, he found that the phlogiston theory was inconsistent with the results from his experiments. He called heat caloric, which was a fluid substance that was constant throughout the universe. Since this fluid could neither be created nor destroyed, this idea uses the principal of conversation of heat.
The caloric theory was very popular during Joule's discoveries, although, Joule's experiments directly conflicted with caloric theory. He found that heat could be created from mechanical work through his experiments.
substance of heat, like one of the classical four elements of the Greeks. To the right, the process of smelting ore is explained with phlogiston.
The caloric theory was produced by Lavoisier in the 1770's. In his papers, he found that the phlogiston theory was inconsistent with the results from his experiments. He called heat caloric, which was a fluid substance that was constant throughout the universe. Since this fluid could neither be created nor destroyed, this idea uses the principal of conversation of heat.
The caloric theory was very popular during Joule's discoveries, although, Joule's experiments directly conflicted with caloric theory. He found that heat could be created from mechanical work through his experiments.
The caloric theory was produced by Lavoisier in the 1770's. In his papers, he found that the phlogiston theory was inconsistent with the results from his experiments. He called heat caloric, which was a fluid substance that was constant throughout the universe. Since this fluid could neither be created nor destroyed, this idea uses the principal of conversation of heat.
The caloric theory was very popular during Joule's discoveries, although, Joule's experiments directly conflicted with caloric theory. He found that heat could be created from mechanical work through his experiments.