The Fate of the Universe
So the universe is currently expanding, but will it always expand? How
will the universe end? Or will it?
The answers to these questions are still being debated.
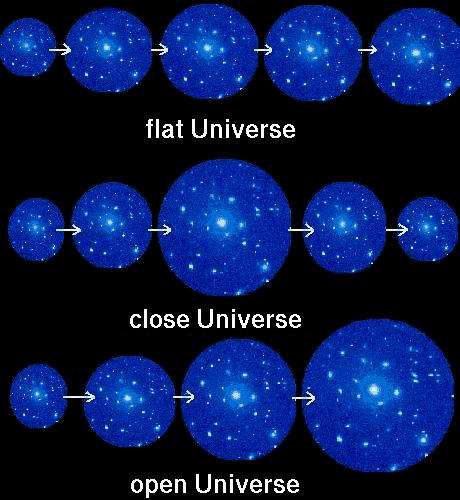
There are three main hypotheses as to how the universe will meet its final
state. These are the Big Crunch theory in which the universe is closed,
the Steady State theory in which the universe is flat, and the Infinite Expansion
in which the universe is open so it expands forever and entropy becomes
infinite.
Big Crunch (closed universe)
If the matter density in the universe is high enough, eventually
the current expansion will be slowed to a halt by the gravitational attraction
of the galaxies and start to contract, ending up by contracting to an infinite
density like a black hole. Is there a high enough matter density in
the universe to cause it to re-collapse in a big crunch? Not if most
of the matter in the universe is visible stars, but this does not appear
to be the case. The answer to this question then depends upon the
amount of matter in the universe that does not give off light.
This matter is referred to as dark matter.
Dark Matter
Astronomers think that there is much more matter in the galaxy, and
the rest of the universe than they can actually see with telescopes. The
way the galaxy behaves gravitationally indicates it has much more mass than
can be accounted for by visible stars alone. A large spherical distribution
of dark matter surrounding the galaxy is thought to contain much of this
missing mass. Perhaps as much as 90% of the matter in the universe is
thought to be dark matter. There have been many hypotheses about the
dark matter may consist of, including neutrinos with mass, black holes, brown
dwarf stars, and much else besides.
If the universe re-collapses will time flow backward?
At one time physicist Stephen Hawking thought that in order for
the universe to recolapse to a point it would have to go back to its original
smooth and ordered state. In order for this to happen entropy would have
to decrease, and since the flow of entropy is fundamental to the way we
understand time, it was thought that time would have to flow backwards. However,
it is no longer generally thought that the universe would return to a smooth
and ordered state and so time would not reverse. ( Brief
History of Time , 1988)
Steady State (flat universe)
If there is exactly enough matter density in the universe to
slow the expansion completely, but not make the universe contract then maybe
the universe could asymptotically approach some maximum size and not relocates.
This is very improbable, and is even debated to be theoretically impossible.
Infinite Expansion (open universe)
Will the universe continue expanding forever until entropy becomes
infinite? If there is not enough matter to completely slow or reverse
the expansion then yes. The matter in the universe will keep on
getting more and more spread out and entropy will always increase in accordance
with the second law of thermodynamics until the universe is a smooth flat
completely homogeneous gas.
Background from:
http://kliman.com/Fractals/pages/black%20hole.htm