Capacitance, Inductance, and Diodes
Capacitors, inductors, and diodes are used a lot in circuits and are the three primary components that are added to a circuit beyond resistors and loads.
Capacitors, Inductors, and Resonance
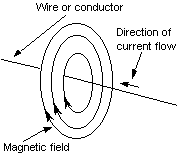
An inductor is the component which is made up of a wire that is wrapped around some type of core many times which opposes the change in electrical current. What this means is that when the current is trying to change the inductor atempts to counter balance that change and in doing so it inducts a voltage across itself. The voltage created is the inductance (in Henrys) times the change in current over the change in time. Now an inductor has many variables which change its inductance from the material which it is composed of to what fills its core.
Capacitors, Inductors, and Resonance
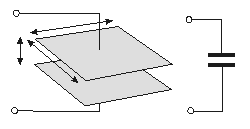
The Capacitor is the component which is made up of two conductors (usually plates) separated by a dielectric material. The capacitor can store an electric charge which can only be done also by a battery. The capacitor stores charge by separating the positive and negative charges which creates and electic field, or voltage. If the voltage varies by time it will make a displacement current in the space previously occupied by the field. The current of a capacitor can be found by taking the capacitance (in Farads) times the change in the voltage over the change in time. The capacitance has variables such as what the material is made of, the area that the plates are, and the space between the plates.
Hyper Physics
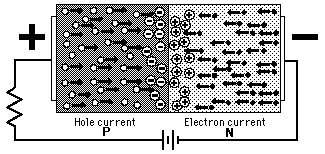
Last but not least are Diodes. To give an idea how a diode works we will go back to the idea of plumbing. Diodes work as valves to allow flow to push the valve open in one direction but close off in the other direction. Diodes have been used since the early 1900's and have been a major element in radio recievers. As seen in the picture above, a diode is split between to parts, the P section and the N section. The N type of the diode is a metal, usually Silicon doped with some other type of element such as phosphorus. The N type has an extra electron in its outershell and therefor is known as the donar because it will be giving up its electron. On the other side is the P type which can be something like Silicon doped with boron. The P type, also known as acceptor, has only 3 electrons in its valence shell and is ready to recieve an electron. When you put these two types together, it creates a valve in which curren can flow from N to P but not in the reverse direction.
To go back to the main menu, click here.