Undoubtedly the most defining feature of
the genre of dubstep is the wobble. This is a technique,
resulting is what is often called the "wub", that uses a
low-frequency oscillator to change key features of the bass,
including the volume, distortion and filter cutoff. By
oscillating the levels of each of these components over time, an
additional rhythm is created using only the extended bass notes,
adding a very unique and singular effect to the resulting sound.
The volume of a sound is very simply
determined by the amplitude corresponding to the oscillating
sinusoidal sound wave that produces the sound.
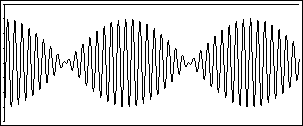
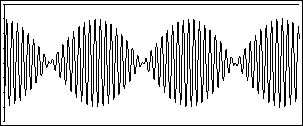
The pulsing, caused by increasing and
decreasing the volume level rhythmically, produces a stimulating
effect. The human brain observes the complex activity of a
pulse and reacts by trying to "dissect" or analyze the sound
that is being picked up by the ears. This results in a
higher levels of "dopamine release[s] during anticipation and
experience of peak emotion to music". [6] Listeners are
stimulated and aroused upon the listening of music, more so when
the anticipation and expectation is higher, another
characteristic of dubstep (Rhythm).
There are many different forms of sound
distortions. Among them, and most commonly found in
differing forms of dubstep, are compression, clipping and
modulation.
The most common form of audio compression
in dubstep involves, of course, the bass. A method called
side-chaining is used. When the volume of a bass track is
raised to the desired level (loud) it results in unwanted peaks
in the master volume distribution, often drowning out the other
instrumental tracks. Side-chaining simple compresses the
bass output, much like a limiter, to ensure the sound does not
exceed the desired threshold. The result is an equalized
and proportional sound without sacrificing the bump of the bass.
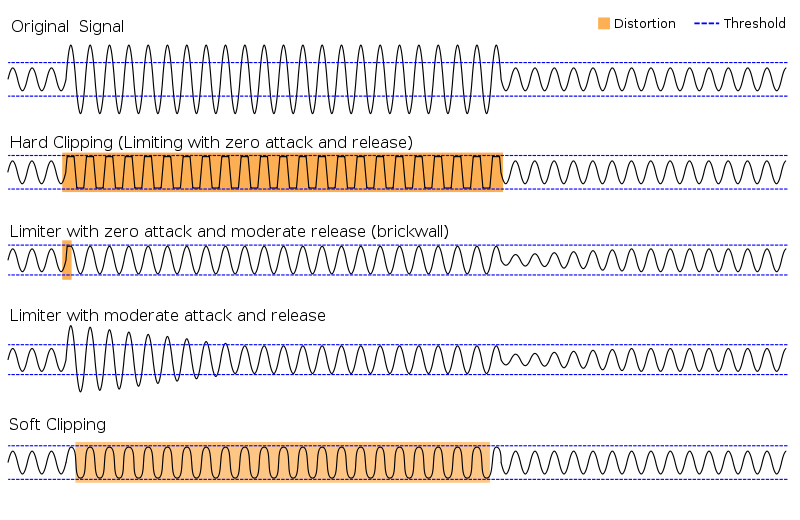
Clipping is another form of distortion that can be seen above
alongside limiting. It has somewhat the same purposes
presented by compressing but a much different result. A
compressor will, as the name implies, compress a sound wave to
match the desired amplitude while a clipper will simply chop off
the portions of the track outside the desired threshold and
connect them, in the most extreme case, with a straight
line. There are levels of clipping ranging from the softest
to the hardest, soft flowing much more smoothly while hard
provides a crunch to the distorted wave. A clear example can
be heard in this video:
The video is also a very clear example of the effect of varying
the amount of clipping distortion is being applied and the effect
that variation has on the sound of the beat.
While volume, compression and clipping all
deal with the amplitude of a wave of sound, modulation seeks to
differ the length of the period of the sinusoidal wave.
When manipulating the length of a single period, it is the
frequency, and therefore the pitch or tone, that is being
altered. Modulation is merely the oscillation of pitch at
differing rates. At high frequencies, low periodical length, the
waves seem to cluster (as seen below), causing higher pitches.
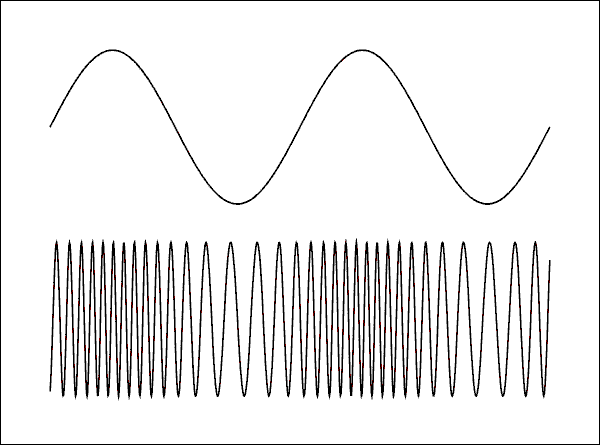
Like distortions, there are many different
filters used in the music industry. There are two filters,
very similar to one another, that hold the position of most
popular among dubstep mixers and DJs alike. They are the
Low-pass filter and High-pass filter. Each of them deal
with limiting the frequencies that output from an input
track. Each will vary the output gain depending on the
frequency, or tone, of the input sound wave. A low-pass
filter will silence the high frequencies and a high-pass filter
will silence the low frequencies. The low-pass filiter is
more common is dubstep, due to the emphasis on the lower and
bassier tones. Usually, a filter will leave the gain of a
track untouched while the frequency is at the desired
level. Once a frequency goes above the cutoff frequency,
however, the filter will start to lower the gain of the track in
a linear fashion.
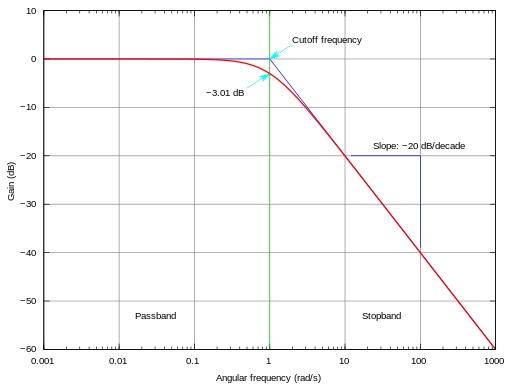
The cutoff frequency is what can be varied
in order to make the wobble effect. The result would be a
differing in the tones that would be projected through the
filter, ranging, of course, from ow to high.
Each of the components of a bass line,
volume, distortion and filter cutoffs, are very important to the
overall sound of the track. When each of them is allowed
to vary, and vary over time, the results can be exciting and
often are revolutionary in the development of modern music.
Home Page
Rhythm
Tonality
The Drop
Bibliography