Evolution of Stars
A star forms in a giant cloud of
interstellar particles. This dust is held together by molecular
attractions. The dust is categorized into two classes, carbon
atoms and "ices" which consist of methane, water and ammonia in small
frozen pieces. Gravitational forces are responsible for pulling
these interstellar particles together to form the mass of a star.
A protostar is formed in the beginnings of a star. The
protostar's gravity is responsible for making stars dense. As the
gravity of the protostar increases so does the contraction of
mass. As the density increased so did the temperature. Eventually
the increase in temperature causes the contraction forces to stop.
When a protostar reaches the point where the contraction stops and
nuclear fusion begins to take place it is then officially a star.
Nuclear fusion creates a balance with the stars natural desire to
contract with forces that push the star apart. At this phase the
star is named main sequence.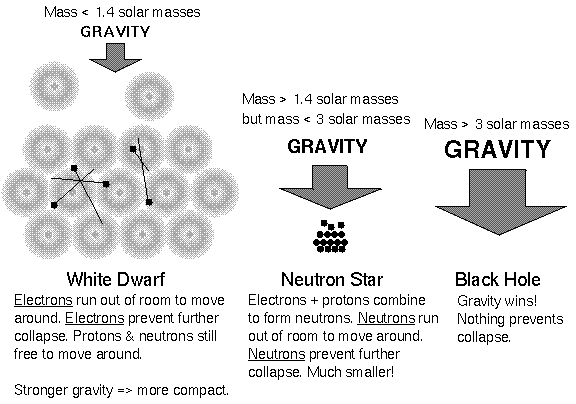
Stars go through the process of turning mass energy into kinetic
energy. Nuclear fusion is the fuel of the stars. Turing
hydrogen into helium creates energy. When the proton source in
the core is exhausted the star will begin to move the fusion process to
outside the core and engulf the core. Fusion continues to take
place and moves further and further away from the core. Unfortunately
for the star this process does come to an end when there is no more
hydrogen to consume. When the core is exhausted and no longer
producing energy and the core begins to shrink. This shrinkage is
a process of the gravitational force no longer being opposed.
As the gravitational force
increases, the star is fusing more protons, at a faster rate than the
star has experienced during its existence. The outward appearance of
the star is deceiving, the increase in the amount of energy causes the
outer layers of the star to expand and grows both in size and
luminosity. At this state the star is called a red giant.
Red is the most typical color for red giants and is caused by the low
temperatures of the gases. Eventually the heat from the core will
push the gas completely away. When the helium core is exposed and
the outer gases are no longer part of the red giant, the state of the
star is named a planetary nebula.
A white dwarf is result of a
planetary nebula of a star made primarily
out of carbon. A star made primarily out of neutrons will turn
into a neutron star when it collapses.

