An Introduction to Lasers
A laser is, in short,
a concentrated beam of light at a single frequency. We will now discuss
how lasers are created and their importance in regard to holography. A material,
which could be any typed of “doped” glass, is shaped into a rod. Around
this rod, a flash tube is wrapped in a helical shape, which emits very short,
intense bursts of broadband light. Some of the atoms in the rod absorb this
light and get excited. That is, they are placed in an energy state, which
is at a higher energy level than their normal state. The energy remains stored
in these excited atoms until they release their stored energy in the form
of light waves and then return to their normal energy state.

http://www.technology.niagarac.on.ca/courses/tech238g/Lasers.html
This is important because
Niels Bohr suggested that the radiation of spectral lines that were created
by atoms could be explained by assuming that the electrons moved about the
nucleus in a fixed orbit. Each of these different orbits represented a different
energy level. When an electron moves to a higher orbit, the electron is
in a higher state of energy. When that electron returns to its lower orbit,
energy is radiated on the form of spectral lines that are characteristic
of a particular atom. That is, different atoms, because of the structure
of their valence electrons, would give off light at a particular frequency.

http://library.thinkquest.org/16468/
hydro-a1.htm?tqskip1=1&tqtime=1125

http://biz.howstuffworks.com/laser2.htm
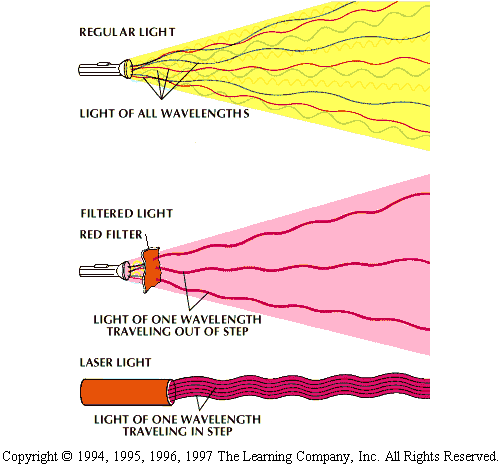
Laser light source material
provides a particular form of energy state in which the excited atoms can
and do pause before returning to the ground state. They stay in this state
until stimulated into returning to the ground state. In this last step,
they emit light having exactly the same wavelengths as the light, which
triggered them into leaving that state. Basically, the atoms are stimulated
into emitting; energy is first stored in the atom and later released by
it when it transfers from the “paused” state to the lower one in the form
of single wavelength light energy. Because the speed of light is constant,
the frequency is also constant. The constant frequency that a laser generates
will later become important.
http://www.technology.niagarac.on.ca/courses/tech238g/Lasers.html
Index
How Lasers and Light Waves make Holograms