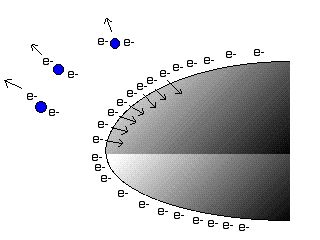
Electrons on the Van de Graff generators dome push against the electrons in the nearby air molecules.
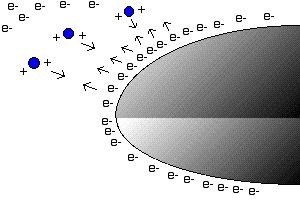
The electrons in the nearby air molecules run away from the larger charge on the Van de Graff generators dome. Leaving the air positively charged or ionized.
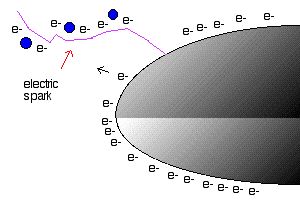
When there is enough attraction in the surrounding air and or a path to ground is provided the electrons leap off the domb and through the air leaving the domb discharged, the nearby surrounding air neutralized, but the net not so distant air with an extra negative charge.