
Courtesy of TutorVista.com
http://www.tutorvista.com/content/biology/biology-iv/locomotion-animals/skull.php
When
speaking of the physics involved in chewing, it is important
to first understand how our lower jaw (also called the
mandible) works. In terms of the physics of our jaw, we can
actually think of our jaw as a lever. When we are chewing
food, or even just opening and closing our mouth when
speaking, only our lower jaw is moving; our upper jaw is not
jointed but is fixed in place to the rest of our skull.
Therefore, our lower jaw operates as a lever of sorts.
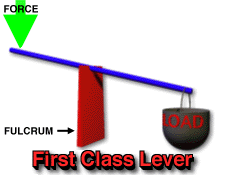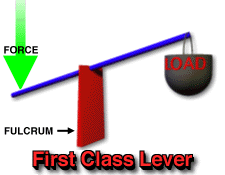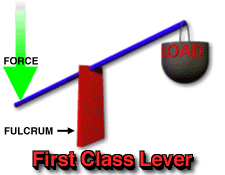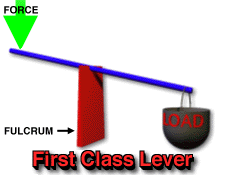
Before we proceed any further on this topic, we should first explain that there are three different classes of lever, each having three parts and a different set-up than either of the others. The three parts of a lever and what they refer to are stated by Questacon Imagination Factory as, "...effort (the force being put into the lever system)...load (the object or resistance that the effort force is acting against, and...fulcrum (the pivot point that the lever turns around). Below is an illustration showing the different classes of lever (1st, 2nd, and 3rd), a brief explanation concerning the differences between them, and examples of everyday items which are considered each kind of lever.
As stated previously, our bottom jaw behaves as a lever; in fact, according to an online pamphlet written by the Questacon Imagination Factory, our jaw actually acts as two different classes of lever depending on what we are using it for at the time. They go on to explain: "When you bite using your front teeth, such as munching a bite out of an apple, your lower jaw acts as a third class lever. When you crunch on the apple with your molars, your lower jaw now acts as a second class lever."
In order to visualize the truth of this statement, we can think of the food as the "load" in these cases and our jaw joint as the "fulcrum". When we bite an apple, the food is at the front of our jaw, and effort is being applied in a upward direction at the middle of the lever arm, as in the illustration above for a 3rd-class lever. Once we move the food to our molars in order to grind it in preparation for swallowing, our jaw is now working as a 2nd-class lever: the fulcrum is still at the same point (our jaw joint), but now the food ("load") is approximately in the middle of the lever arm and the effort is being applied upward and is at the far end of the lever arm from the fulcrum.
It is also important to note that there is another aspect of physics which is involved in chewing: torque. The Questacon Imagination Factory pamphlet describes torque as, "...a rotational force that is influenced by two factors - the length of the arm that's being rotated, and the strength of the force that is acting on the arm from a direction that is perpendicular to the arm." They go on to give the equation of torque as: "Torque = length of arm (m) x perpendicular force (N)". This means that the longer the lever arm (represented in this case by our lower jaw), the more torque your jaw is capable of producing. Therefore, people who have a longer lower jaw create more torque when they chew.
Before we proceed any further on this topic, we should first explain that there are three different classes of lever, each having three parts and a different set-up than either of the others. The three parts of a lever and what they refer to are stated by Questacon Imagination Factory as, "...effort (the force being put into the lever system)...load (the object or resistance that the effort force is acting against, and...fulcrum (the pivot point that the lever turns around). Below is an illustration showing the different classes of lever (1st, 2nd, and 3rd), a brief explanation concerning the differences between them, and examples of everyday items which are considered each kind of lever.
http://imaginationfactory.questacon.edu.au/assets/im_levers.pdf |
http://discover.edventures.com/images/termlib/f/first_class_lever/support.gif
 http://discover.edventures.com/images/termlib/s/second_class_lever/support.gif
 Animations courtesy of
user
Sujin01pd2017
http://discover.edventures.com/images/termlib/t/third_class_lever/support.gif |
-1st class levers are situated with the load on one end, the fulcrum or pivot point in the center of the lever arm, and the effort applied to the end of the lever opposite from the load. The load and the effort are both applied downward on the lever arm, while the fulcrum is underneath. Examples of 1st-class levers include see-saws and scissors. -2nd-class levers are situated with the fulcrum under one end, the effort applied upward under the other end, and the load pressing down in the middle of the lever arm. Examples of 2nd-class levers are doors and wheelbarrows. -3rd-class levers are those in which the fulcrum lies underneath one end, the effort applied is located in the middle of the lever arm and is being applied upwards, and the load is situated at the end opposite the fulcrum and is applying a force downwards. Examples of this kind of lever are such things as spoons and golf clubs. |
As stated previously, our bottom jaw behaves as a lever; in fact, according to an online pamphlet written by the Questacon Imagination Factory, our jaw actually acts as two different classes of lever depending on what we are using it for at the time. They go on to explain: "When you bite using your front teeth, such as munching a bite out of an apple, your lower jaw acts as a third class lever. When you crunch on the apple with your molars, your lower jaw now acts as a second class lever."
In order to visualize the truth of this statement, we can think of the food as the "load" in these cases and our jaw joint as the "fulcrum". When we bite an apple, the food is at the front of our jaw, and effort is being applied in a upward direction at the middle of the lever arm, as in the illustration above for a 3rd-class lever. Once we move the food to our molars in order to grind it in preparation for swallowing, our jaw is now working as a 2nd-class lever: the fulcrum is still at the same point (our jaw joint), but now the food ("load") is approximately in the middle of the lever arm and the effort is being applied upward and is at the far end of the lever arm from the fulcrum.
It is also important to note that there is another aspect of physics which is involved in chewing: torque. The Questacon Imagination Factory pamphlet describes torque as, "...a rotational force that is influenced by two factors - the length of the arm that's being rotated, and the strength of the force that is acting on the arm from a direction that is perpendicular to the arm." They go on to give the equation of torque as: "Torque = length of arm (m) x perpendicular force (N)". This means that the longer the lever arm (represented in this case by our lower jaw), the more torque your jaw is capable of producing. Therefore, people who have a longer lower jaw create more torque when they chew.
Table of Contents
Title Page
Page 1: Introduction to Teeth
Page 2: Tooth Correction
Page 4: Tooth Facts
Bibliography

Animation Library
http://www.animationlibrary.com/animation/28598/Tooth_dances/
Title Page
Page 1: Introduction to Teeth
Page 2: Tooth Correction
Page 4: Tooth Facts
Bibliography

Animation Library
http://www.animationlibrary.com/animation/28598/Tooth_dances/