|
Renewable Energy for the Future Ryan Peterson Physics 102 April 25, 2008 |
|
How it Works |
|
The Earth has a lot of heat left over from its creation. Over time this heat is released through natural processes. This heat is not equally accessible in all areas of the world. For this reason Geothermal Power Plants are limited geographically to areas where this heat can be easily accessible, typically around natural hot spring and geysers systems.
Typical coal fired power plants burn coal to heat water into steam, and use that steam to drive turbines, which produce electrical power. Geothermal Power Plants utilize naturally heated steam in a similar manner. |
|
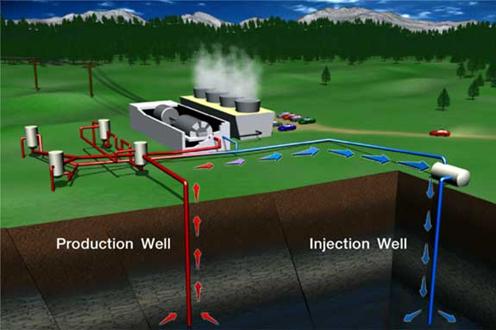
A typical geothermal power plant layout. Image courtesy of: Geothermal Education Office Direct Link: http://geothermal.marin.org/GEOpresentation/sld037.htm
|
|
Typical fossil fuel power plants have negative environmental impacts including the release of CO2 into the atmosphere, and the ever-present danger of an oil spill, or other release. Geothermal power plants produce no pollution. Water used to power the turbines can be captured and re-injected into the ground, thus maximizing the longevity of the heated water supply. Other plants use this water to provide heating to surrounding facilities. |