A
rocket engine is
not like a conventional engine. A conventional engine ignites
fuel which then pushes on some pistons, and it turns a crank.
Therefore, it uses rotational energy to turn the wheels of the
vehicle. Electric motors also use rotational energy to turn fans,
and spin disks. A rocket engine does not use rotational energy to
run. They are reaction engines. The principle of it is that
the fuel contained within the body of the rocket goes through a
chemical reaction as it comes out of the end of the rocket. This
reaction then causes thrust and propels the rocket forward. This
is an example of one of Sir Isaac Newton's fundamental laws. "For
every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction" (How Rocket
Engines Work.)


This is a
representation of Newton's law.
(http://www.howstuffworks.com/rocket.htm/)

This is a picture of a space shuttle rocket engine during a test burn.
Notice the blue flame of the fuel igniting. This cause thrust, and pushes
the rocket in the opposite direction.
(http://www.howstuffworks.com/rocket.htm/)
Solid Fuel Rockets
Liquid Fuel Rockets
(http://www.howstuffworks.com/rocket.htm/)

This is a picture of a space shuttle rocket engine during a test burn.
Notice the blue flame of the fuel igniting. This cause thrust, and pushes
the rocket in the opposite direction.
(http://www.howstuffworks.com/rocket.htm/)
The strength of a
rocket is measured in pounds of thrust. A pound of thrust is the
amount of force required to keep a one pound object stationary against
gravity (How Rocket Engines Work.) In order to generate this
thrust,
rockets burn one of two types of fuel, solid fuel or liquid fuel.
Because of this fact, rockets are often classified by the type of fuel
that they burn.
Solid Fuel Rockets
Solid fuel rockets
are the first rockets to be recorded in history. They were first
invented in ancient China, and have been used ever since (How Rocket
Engines
Work.) The chemical make up of a solid rocket fuel is very
similar to the chemical makeup of gunpowder. However, the exact
chemical make up is not the same. To make a rocket work, a fast
burning nonexclusive fuel is needed. Gunpowder explodes, making
it unusable. So the chemical composition was altered to make it
burn fast, but not explode. One of the biggest problems with
solid
fuel rocket engines is that once started, the reaction cannot be
stopped
or restarted. This makes them considered uncontrollable.
Therefore, solid fuel rockets are more widely used for missiles, or as
booster rockets.
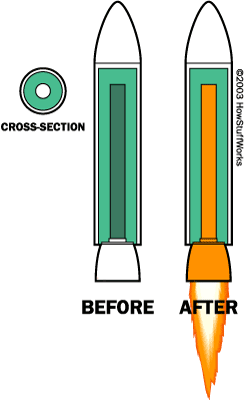

This is a diagram of
how A solid fuel rocket engine looks before and after ignition.
The solid fuel is in dark green, and then in orange as it is ignited to propel the rocket.
(http://www.howstuffworks.com/rocket.htm)
The solid fuel is in dark green, and then in orange as it is ignited to propel the rocket.
(http://www.howstuffworks.com/rocket.htm)
Liquid Fuel Rockets
The first liquid fuel
rocket was produced by Robert Goddard in 1926 (How Rocket Engines
Work.) The idea of liquid fueled rocket is easy to grasp. A
fuel and an oxidizer ,in Goddards case he used gasoline and liquid
oxygen, are pumped into a combustion chamber. A reaction takes
place, and it expands propelling the rocket forward. The
expanding gas is then forced through a nozzle that makes them
accelerate
to a higher velocity (How Rocket Engines Work.)


This diagram is a
basic model of how a
liquid fuel rocket engine works.
It is easy to see that a liquid fueled rocket is much more complex that a solid fueled one.
(http://www.howstuffworks.com/rocket.htm)
Home
Introduction
Rocket Bodies and Nose Cones
Practical Application
Bibliography
It is easy to see that a liquid fueled rocket is much more complex that a solid fueled one.
(http://www.howstuffworks.com/rocket.htm)
Home
Introduction
Rocket Bodies and Nose Cones
Practical Application
Bibliography